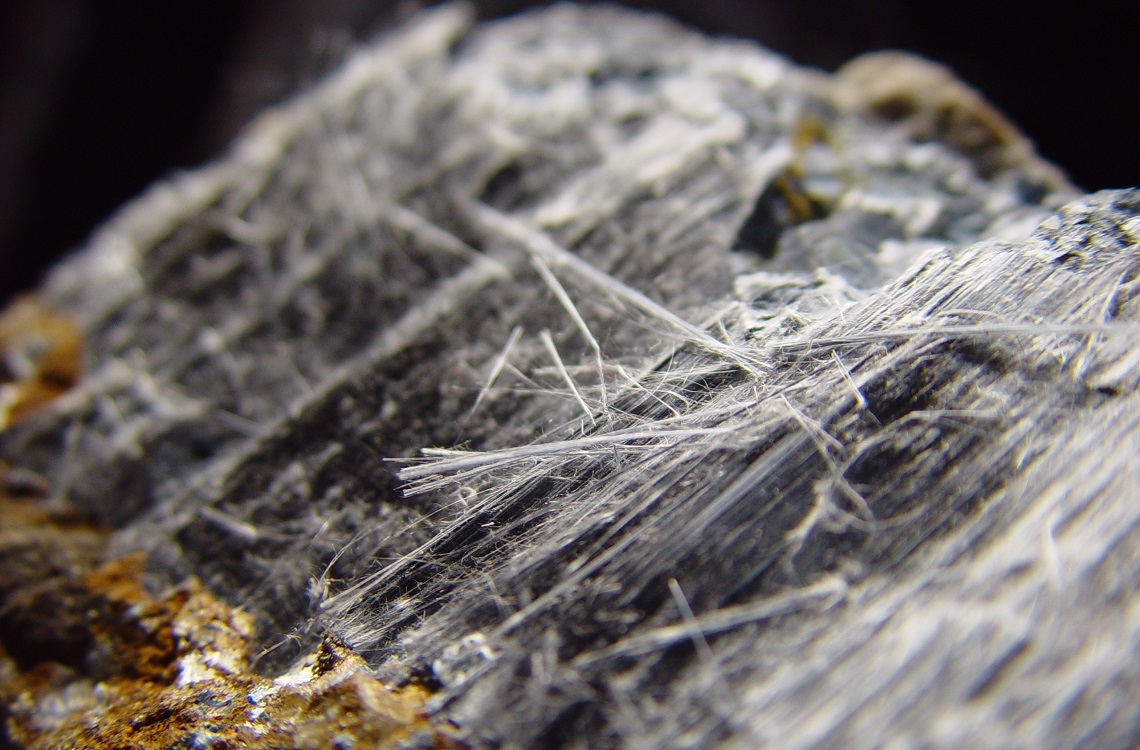
Asbestos is a term used to refer to six naturally occurring silicate minerals. All are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic ‘fibrils’ that can be released into the atmosphere by abrasion and other processes. Asbestos is an excellent electrical insulator and is highly heat-resistant, so for many years it was used as a building material. However, it is now a well-known health and safety hazard and the use of asbestos as a building material is illegal in many countries. Inhalation of asbestos fibres can lead to various serious lung conditions, including asbestosis and cancer.
Archaeological studies have found evidence of asbestos being used as far back as the Stone Age to strengthen ceramic pots, but large-scale mining began at the end of the 19th century when manufacturers and builders began using asbestos for its desirable physical properties. Asbestos was widely used during the 20th century until the 1970s, when public recognition of the health hazards of asbestos dust led to its prohibition in mainstream construction and fireproofing in most countries. Despite this, and in part because the consequences of exposure can take decades to arise, at least 100,000 people per year are thought to die from diseases related to asbestos exposure.
We conduct Asbestos/Hazmat Survey on your ships or facilities, after getting result of Asbestos from our accredited laboratory or IHM report, Before process, We conduct job safety analysis, risk evaluate and safe manner works, our professional team provide safe work as set up quarantine on your ships or facilities. After all safe works you will get International Valid Asbestos Free Certificate, You can be sure that getting professional service scope international and national laws, standards and regulations like OSHA & NIOSH from us.
Our professional team conduct to remove and dispose the other hazmats as ODS, Rockwool, Lead and Lead Compounds, Mercury, Radioactive Substances etc. all hazmats in IHM report part I,II and III.
Our team has qualification for conduct Asbestos Investigation and IHM Report.
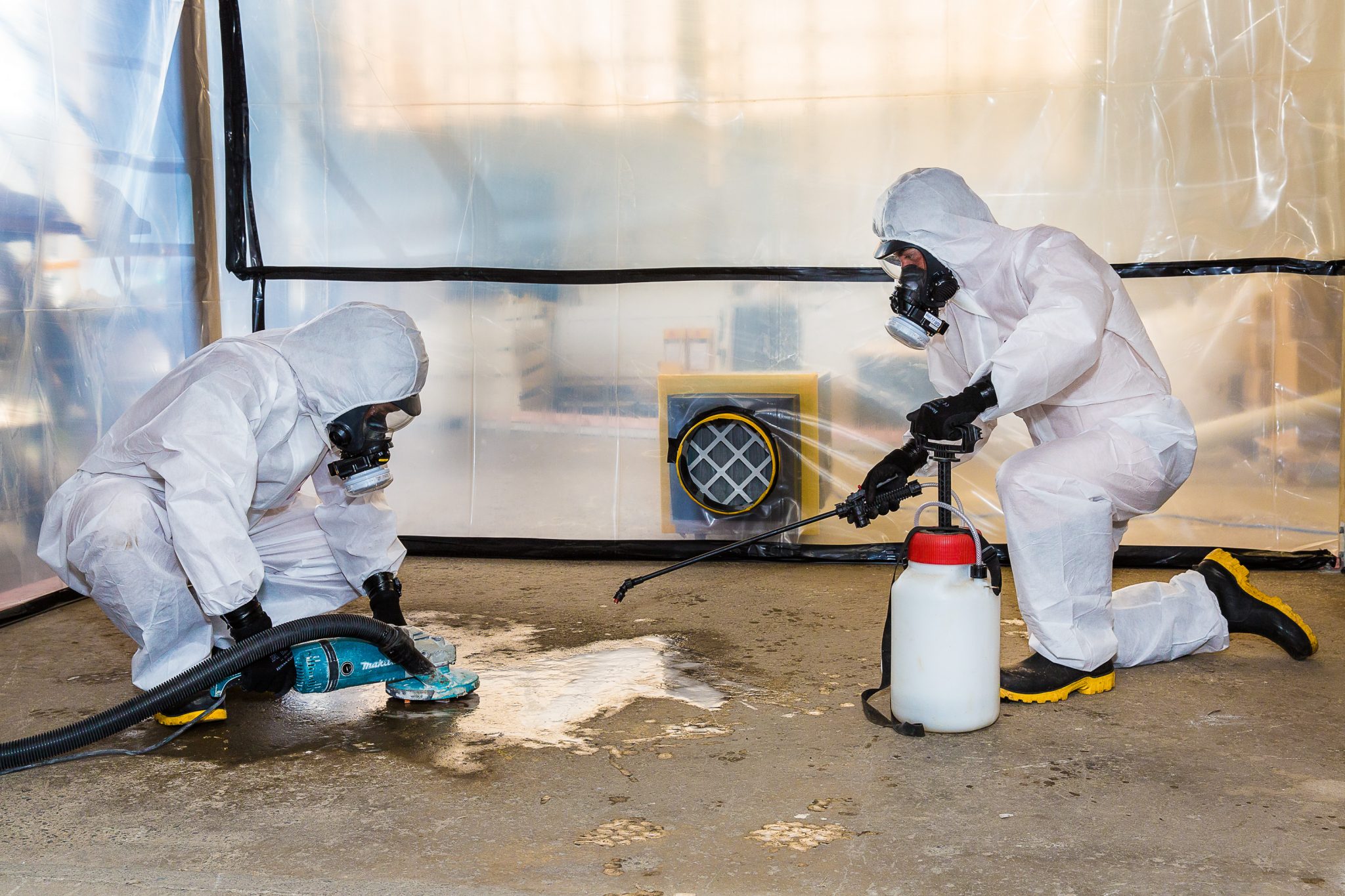


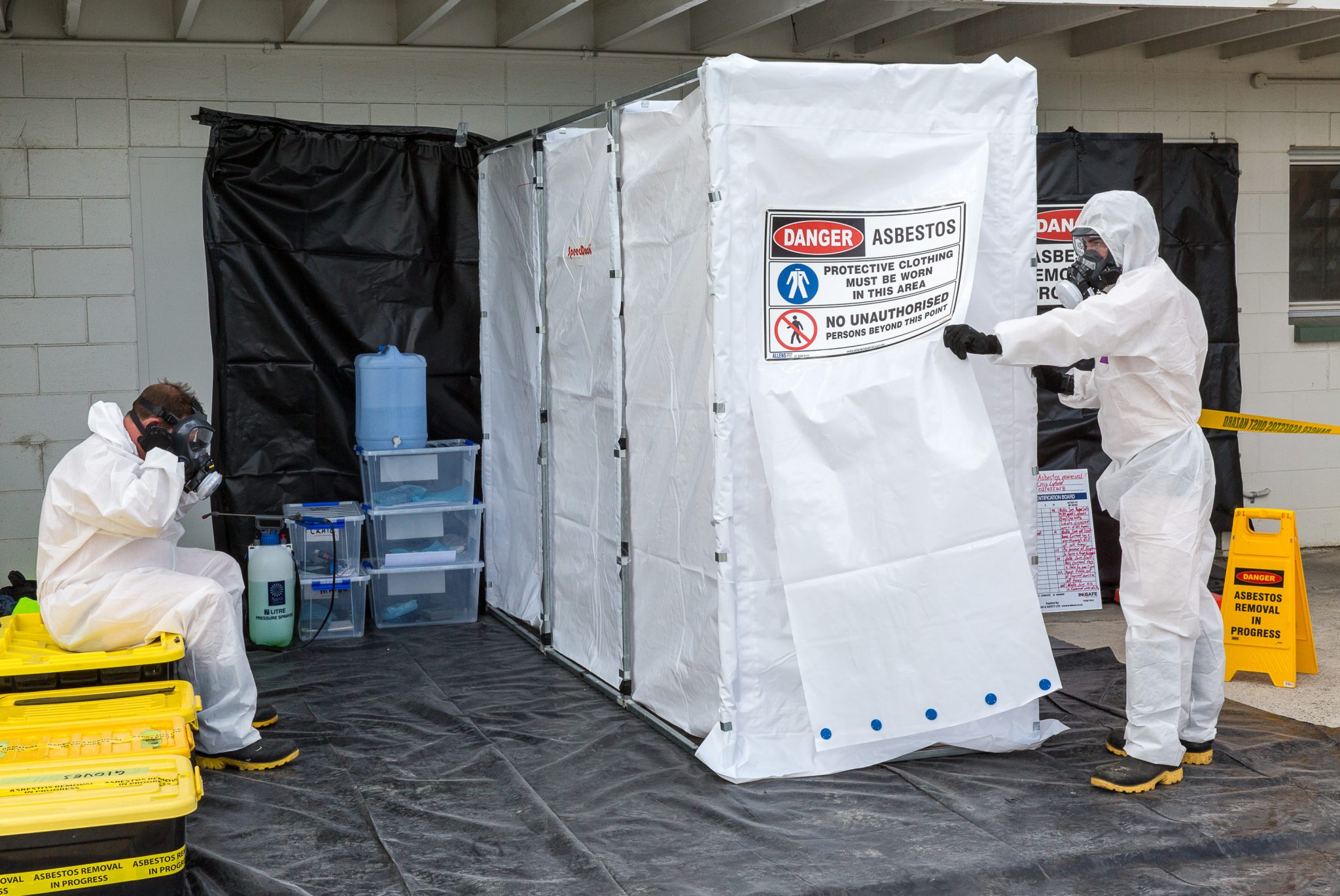

The OSHA standard establishes a classification system for asbestos construction work that spells out mandatory, simple, technological work practices that employers must follow to reduce worker exposures. Under this system, the following four classes of construction work are matched with increasingly stringent control requirements:
For all covered work, employers must use the following control methods to comply with the PEL and STEL:
Employers must use the following engineering controls and work practices for all operations regardless of exposure levels:
The following work practices and engineering controls are prohibited for all asbestos-related work or work that disturbs asbestos or PACM regardless of measured exposure levels or the results of initial exposure assessments: